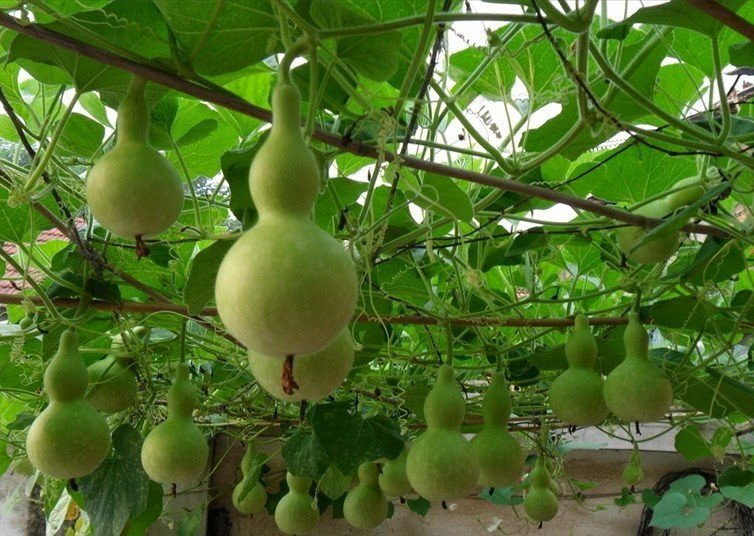
The Calabash, Lagenaria siceraria (synonym Lagenaria vulgaris Ser.), also known as opo squash, bottle gourd or long melon is a vine grown for its fruit, which can either be harvested young and used as a vegetable, or harvested mature, dried, and used as a bottle, utensil, or pipe. The fresh fruit has a light green smooth skin and a white flesh. Rounder varieties are called calabash gourds. They come in a variety of shapes, they can be huge and rounded, or small and bottle shaped, or slim and serpentine, more than a metre long.
Known more in the Chinese regions and Indian subcontinents, bottle gourd has many names in local dialects such as hulu, calabash, lauki, laau, dhudhi, hyotan, hisago etc.
The calabash was one of the first cultivated plants in the world, grown not primarily for food, but for use as a water container. The bottle gourd may have been carried from Africa to Asia, Europe and the Americas in the course of human migration, or by seeds floating across the oceans inside the gourd. It has been proven to be in New World prior to the arrival of Columbus. It shares its common name with that of the calabash tree (Crescentia cujete).
Bottle gourd has been archaeologically known to be used since 11,000 to 13,000 years and has served as a popular vegetable in the Asian regions for a long time. The recent researches that have revealed its medicinal properties such as digestion improvement and weight loss are resulting into worldwide popularity of it.
 Health benefits
Health benefits
Various old medicinal systems such as Ayurveda, have praised gourd for nutrient rich contents and their magical effects in many health ailments including high blood cholesterol, diabetes, overweight, digestive problems. However, recent researches have shown a significant need to check the quality of the vegetable as some of these might be toxic and can have a fatal impact on our health. Lets find out more health related facts about bottle gourd and reap maximum benefits out of it.
Approximate 96% of water content in bottle gourd makes it ideal for extracting juice. It is enriched with dietary fiber, vitamins such as vitamin B and vitamin C, minerals like sodium, potassium, Iron, etc. Low in fat and cholesterol, and full of many healthy contents, makes a strong reason to include bottle gourd juice in our regular diet. To prepare a healthy bottle gourd juice, take a fresh bottle gourd, and taste a slice to ensure it is not bitter. Then peel it and chop into small pieces and put them into the juicer. Now drink the fresh juice to enjoy its wonderful health benefits. Optionally you can also strain the juice and can also add a pinch of salt or pepper to enhance the taste.
Caution
A case of “Bottle gourd poisoning” has came in the notice when 59-year-old Sushil Kumar Saxena, Deputy Secretary in the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research, died in a hospital after consuming a glass of bottle gourd and bitter gourd juice in June 2010. An expert committee was constituted by the Health Ministry to study the possible side effects of bottle gourd, confirmed the death by bottle gourd poisoning.
Since then, a public advisory has been issued which says: “A slice of bottle gourd should be tasted before extracting the juice to ensure that it is not bitter. If bitter, it should be discarded and not be consumed.” Bitter bottle gourd carries a highly toxic compound named “Tetracyclic Triterpenoid Cucurbitacins” that can cause serious side-effects. If one faces any symptoms of nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, gastrointestinal bleeding after consumption of bottle gourd juice, he should be rushed to the nearest hospital immediately.
However, the plant is not normally toxic when eaten and is safe to consume. The excessively bitter (and toxic) gourds are due to improper storage (temperature swings or high temperature) and over-riping.
Do not mix bottle gourd juice with other vegetable juices – The advisory also suggests not mixing bottle gourd juice with any other vegetable juice so as not to mask calabash’s taste if it has gone bad.
Bottle Gourd Juice for Weight Loss
Consuming cooked bottle gourd or bottle gourd juice shows its effects in cooling, calming and easy digestion.Fiber supports the digestive system and prevents constipation and its related disorders like flatulence and piles. This vegetable is also recommended by ayurvedic practitioners for liver inflammation and to support the liver to efficiently process food for maximum absorption of nutrition.
Low in calorie and fat it is also great for weight loss and high cholesterol levels. Recently, bottle gourd has gained the importance for its weight losing properties. Since bottle gourd is high in water and dietary fiber, drinking a cup of bottle gourd juice in morning empty stomach gives a good fiber rich start to the day. While juice of a 100 gm bottle gourd only provides you as low as 14 calorie, it helps to curb the hunger pangs in morning and restrict you from over eating in the breakfast.
If you are drinking bottle gourd juice for weight loss, then you should not strain the juice as the weight loss properties are mainly because of its fiber content which gets filtered in the straining process. Also bottle gourd juice with a fruit bowl is a healthy replacement of unhealthy high calorie snacks in afternoon.
Bottle Gourd Juice for Heart Problems
High in sodium and potassium, bottle gourd is an excellent vegetable for hypertension patients. Many health experts and naturopaths suggest that drinking bottle gourd juice benefits to high blood pressureand heart patients. Regular consumption of a cup of bottle gourd juice with a glass of water on an empty stomach in early morning helps to reduce the high blood pressure and cholesterol levels and makes the heart healthy.
Bottle Gourd Juice for Diabetics
Bottle gourd or Lauki juice is an excellent remedy for the excessive thirst caused by diabetes, diarrhea,and over consumption of fatty foods. A glass of bottle gourd juice with a pinch of salt quenches the thirst, prevents fatigue due to loss of sodium and keeps you refreshed in summers.
As per Ayurveda, consuming a glass of bottle gourd juice in early morning prevents and treatspremature graying of hair.
Culinary and other uses of Bottle gourd:
Cooking Tips
- Grate a bottle gourd and squeeze out the juice. Mix it with a teaspoonful of lime juice and include in your daily diet.
- Julienne a bottle gourd and steam it lightly. Add it to a bowl of yoghurt, along with a pinch of salt.
- Due to its delicate and nutty flavor, calabash gourd is used for preparing many delectable recipes, including hot curries.
- The vegetable is used as a stir-fry or in the soup in the southern Chinese cuisine.
A popular north indian dish is lauki channa, (channa dal and diced gourd in a semidry gravy). In Maharashtra, the skin of the gourd is used in making a Chutney preparation.
In Vietnam, it is called bầu canh or bầu nậm, and is used in a variety of dishes: boiled, stir-fried, soup dishes and as a medicine. The shoots, tendrils, and leaves of the plant may also be eaten as greens.
In Bangladesh, it is called lau. In Nepali, it is called lauka. In Arabic, it is called qara. In Aramaic, it is called qura. In the Talmudic period the young were boiled, whilst the mature fruit are eaten as desert. The tender young gourd is cooked as a summer squash.
In Central America, the seeds of the calabash gourd are toasted and ground with other ingredients (including rice, cinnamon, and allspice) to make the drink horchata. Calabash is known locally asmorro or jícaro. In Colombia and Venezuela, the calabash is known as a tapara or totuma.
In parts of India, the dried, unpunctured gourd is used as a float (called surai-kuduvai in Tamil) to learn swimming in rural areas. Indian musical instruments, such as the tanpura, sitar and rudra veena, are constructed from dried calabash gourds, using special cultivars that were originally imported from Africa and Madagascar. They are mostly grown in Bengal and near Miraj, Maharashtra. These gourds are valuable items and they are carefully tended, sometimes they are given injections to stop worms and insects from making holes while they are drying, etc.
In Pakistan, the green Calabash is known as Lauki while the yellow variety is known as kaddu in Urdu.
Hollowed out and dried calabashes are a very typical utensil in households across West Africa. They are used to clean rice, carry water, and as food containers. Smaller sizes are used as bowls to drink palm wine.
In Peru, Bolivia and Ecuador, calabash gourds are known to have been used for medicinal purposes for over a thousand years by Andean cultures. The Inca culture applied folklore symbology to gourds to pass down from one generation to another, and this practice is still familiar and valued.
Hindu ascetics (sadhu) traditionally use a dried gourd vessel called the kamandalu. The juice of bottle gourd is considered to have medicinal properties and to be very good for health. The Baul singers of Bengal have their musical instruments made out of it. The practice is also common among Buddhistand Jain sages.
The Ivy gourd or Bimbi (Sanskrit name) the Coccinia grandis, is also known as dondakaya, kovakkai and tindora; baby watermelon, little gourd, gentleman’s toes is a tropical vine. It is also known asCephalandra indica and Coccinia indica. Kundru is a Indian local name of Ivy Gourd. It is under cultivation as vegetable crop in Chhattisgarh, India. Coccinia grandis native range extends from Africa to Asia, including India, the Philippines, China, Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, Vietnam, eastern Papua New Guinea, and the Northern Territories, Australia. In Southeast Asia, ivy gourd is grown for its edible young shoots and edible fruits.
Medicinal value
In traditional medicine, fruits have been used to treat leprosy, fever, asthma, bronchitis and jaundice.The fruit possesses mast-cell stabilizing, anti-anaphylactic and antihistaminic potential. Extracts of the Indian herb Coccinia indica reduced blood sugar levels by almost 20 percent in a study conducted by researchers from the Institute of Population Health and Clinical Research in Bangalore and were published in the journal Diabetes Care.
“This study suggests that C. cordifolia extract has a potential hypoglycemic action in patients with mild diabetes,” the researchers said. “However, further studies are needed to elucidate mechanisms of action.” According to the researchers, a person would have to eat 50 grams (2 ounces) of the cooked vegetable per day to receive the same benefit as taking 1 gram of the extract.
Ivy gourd extracts and other forms of the plant can be purchased online and in health food stores. It is claimed that these products help regulate blood sugar levels. There is some research to support that compounds in the plant inhibit the enzyme glucose-6-phosphatase. Glucose-6-phosphatase is one of the key liver enzymes involved in regulating sugar metabolism. Therefore, ivy gourd is sometimes recommended for diabetic patients. Although these claims have not been supported, there currently is a fair amount of research focused on the medicinal properties of this plant focusing on its use as anantioxidant, anti-hypoglycemic agent, immune system modulator, etc. Some countries in Asia like Thailand prepare traditional tonic like drinks for medicinal purposes.
Among other health benefits of this plant: the raw Fruits, which are chewed to cure mouth sores, the fruits are also used for treating coughs. Leaves are used for the treatment of boils and skin eruptions. It also helps to stimulate the digestion and bowel movements. The leaves are used for treating some kidney disorders. It is quite effective in the treatment of certain Sexually Transmitted Diseases, like syphilis. A paste made of leaves is applied to the skin to treat scabies. In Bangladesh, the Roots are used to treat osteoarthritis and joint pain.
Recipes
There are a variety of recipes from all over the world that list ivy gourd as the main ingredient. It is often compared to bitter melon. The fruit is commonly eaten in Indian cuisine. People of Indonesia and other southeast Asian countries also consume the fruit and leaves. In Thai cuisine it is one of the ingredients of the Kaeng khae curry. Cultivation of ivy gourd in home gardens has been encouraged in Thailand due to it being a good source of several micronutrients, including vitamins A and C.
In India it is eaten as a curry, by deep-frying it along with spices; stuffing it with masala and sauteing it, or boiling it first in a pressure cooker and then frying it. It is also used in sambar, a vegetable and lentil-based soup.
Here is one interesting healthy Indian preparation, you will need: Kundru fruits, Chana Dal (chickpea splitted seeds), Methi (fenugreek), Lason (garlic), Mirch (chilli), Haldi (turmeric), Dhania (coriander), Namak (salt), Tel (cooking oil). Method of Preparation: Kundru fruit is cut into two pieces and seeds are separated. After this, the fruit is washed thoroughly in running water. In pan, cooking oil is taken and all the ingredients and Kundru fruits are added. The mixture is cooked in low flame. After cooking, it is served as curry with meals. The natives prepare Kundru curry without adding Chana Dal also, but according to the healers the combination of Kundru fruits and Chana Dal is more promising for diabetics. Among the natives this preparation is popular for its delicious taste and the traditional healers are aware of its health benefits. According to them this preparation is specially useful for the patients having diabetes. It is also useful in biliousness and diseases of blood. During fever the use of this preparation with meals, helps in reducing the high temperature.
The ivy & bottle gourds
The healers claim that the Kundru fruits are having the capacity to reduce extra fat. Also, its regular useflushes out the toxic material from body. But there is a common belief among the natives that the consumption of raw Kundru fruits results in deafness. The healers are aware of this fact. They suggest the natives to consume it with common salt (namak). Its combination with namak, nullifies its harmful effects. Kundru fruits consumed in form of spicy curry are although good in taste but it do not reduce the obesity in this form. Ivy gourd is also rich in beta-carotene.
Using Ivy Gourd supplements safely:
Little is known about the safety of taking ivy gourd supplements in the long term. However, since ivy gourd may lower blood sugar levels, there’s some concern that using ivy gourd in combination with anti-diabetes drugs may have harmful effects. In addition, many medical experts recommend discontinuing use of ivy gourd supplements at least two weeks before undergoing surgery.
If you’re considering the use of ivy gourd in the treatment of diabetes (or any other health condition), make sure to consult your physician. It’s important to note that self-treating a chronic condition with ivy gourd and avoiding or delaying standard care may have serious consequences.

Ash gourd, Benincasa hispida is an extensive trailing or climbing annual herb cultivated throughout the plains of India and on the hills up to 1200 m altitude, as a vegetable. Originally cultivated in South-East Asia, the winter melon is now widely grown in East Asia and South Asia as well. Winter melon is also a common name for members of the Inodorus cultivar group of the muskmelon (Cucumis melo L), more commonly known as casaba or honeydew melons. This plant trails on ground and has hairy leaves. The young fruit is hairy. The fruit loses it hair and gets a waxy coat when matures.
As per Ayurveda classics the herb is known as Kushmanda. Sanskrit names also include: Brihatphala, Pushpaphala, Pitapushpa, etc. & Hindi names: Petha, Alu puhul. It is also used in spiritual practices in some parts of India.
Kushmanda (white gourd) belongs to gourd family of vegetables is commonly known as Petha in India and used as medicine in Ayurveda. Other names are ash gourd, wax gourd because of its outer skin that has wax and ash type layer. Mostly it is used in culinary and in India Petha sweet dish is very popular made from pulp of white gourd and sugar syrup. In Ayurveda its fruit pulp, seeds and seeds oil is used to treat various health problems. According to texts of ayurveda this fruit is very light to digest and sweet to taste. It cools the body and acts as a brain tonic.
Many studies has been done on Ash gourd to support its health benefits:
Winter Melon or Ash gourd is one of the best vegetable as well as a medicine. It is packed with phyto-nutrients and medicinal values. It is used for weight gain therapy, to improve intelligence and so on. In Indian system of medicine, it is hailed as the best among all the fruit-yielding creeper plants.
- As pulp of fruit contains lot of water, vitamin B, C, minerals and fibre so it can be used to treat constipation as pulp of ash gourd has laxative property. This used to improve overall digestion.
- Consumption of pulp can be used to treat urinary dysfunction and it can be very helpful in treatment of kidney stones.
- Ash gourd juice can be taken in morning with same amount of water empty stomach to treat peptic ulcer, do not eat anything for 2-3 hours after drinking this.
- It seeds powder can be used to eject tapeworm and other intestinal worms. Take 3-6 gm before sleeping.
- It can even treat mouth ulcers, protecting teeth and gums when a mouth gargle of the juice is done regularly.
- Pulp and paste of leaves can be used to reduce skin burning sensation.
- White gourd as a brain tonic as well as improves memory. Acts as a tranquilliser and therefore useful in schizophrenia, debility and memory loss. Ash gourd normalizes sleeping pattern and very helpful in patients with insomnia.
- Patients affected by tuberculosis of lungs are benefited by the use of this fruit. It strengthens the lungs and body.
- Seed (5-6 gm) boiled in milk can be take to increase sperm count and it will also improve libido. The pulp of the matured fruit helps to increase quality and quantity of semen. Hence it is used inVajikarana preparations.
- White gourd`s seed powder with mixed with brahmi is really good in treatment of epilepsy in children. Seeds have great nutrition value like other dried nuts.
- Kushmanda helps persons who are recuperating from illness to gain back their lost energy and nutrients.
Culinary uses:
Fruits of this plant are widely used for cooking in India, Pakistan and China. Many delectable dishes like peta, (a sweet dish), soups and curries are prepared by this fruit.
Winter melon ayurvedic properties:
Matured fruit balances all three doshas.
Rasa (Taste): Madhura (sweet)
Guna (qualities): Laghu (light to digest), Snigdha (unctuous, oily)
Vipaka (taste conversion after digestion): Madhura (sweet)
Veerya (potency): Sheeta (cold)
Effect on Tridosha: Balances Pitta Vata
Prabhava (special effect): Medhya – improves intelligence
Uses as per Ayurveda:
Mutraghatahara – helps in easy passing of urine
Pramehashamanam – useful in diabetes, urinary tract disorders
Mutrakuchrahara – useful in dysuria
Ashmarichedana – useful in urinary calculi. Helps to break into pieces
Vinmutra glapanam – helps to increase the bulk of urine and faeces
Trushartishamanam – relieves thirst and related pain
Jeernangapushtidam – nourishes the worn out body parts. Helps to improve body mass.
Vrushyam – aphrodisiac
Arochakahara – relieves anorexia
Balya – improves strength and immunity
Bruhmana – helps to gain weight, provides nutrition
Pittasranut – useful in bleeding disorders due to Pitta imbalance, such as menorrhagia, bleeding per rectum, nasal bleeding etc.
Vatanut – balances Vata
Bastishuddhikara – cleanses bladder
Chetorogahrut – relieves excessive tiredness
The unripe winter melon helps to balance Pitta.
Mid-ripe winter melon is coolant and increases Kapha.
Old winter melon (Fully riped), is not so coolant, sweet, alkaline, easy to digest and improves digestion strength.
Ash gourd seed oil has similar effects to those of the fruit.
Part used: Fruit, seed, seed oil
Dosage: Fruit – 10 – 20 grams, Seed powder – 3 – 6 grams, Seed oil – 5 ml
Spiritual practice with ash gourd:
To symbolize evil power destruction, camphor is lit on the ash gourd fruit and after Arati (circular rotation to the Diety, symbolizing zero-ness (ego-less), ash gourd is usually shattered into pieces by pounding it on to the ground.
This ritual is done on many festivals, usually during inauguration of new buildings, new business, during Lakshmi Pooja etc.
Side effects of Winter melon:
In obese people, it should be used for a limited period, in minimal dose.
It increases Kapha, hence it is not ideal to use this in winter and whenever someone has cold, asthma or bronchitis.
However, it is very useful in post tuberculosis recuperation period. It improves weight. If it is sweet, it is not ideal during indigestion.