According to a recent study, it has been discovered that high levels of vitamin D can decrease the occurrence of colorectal cancer.
 Colorectal cancer is found in either the colon or the rectum. Colon cancer and rectal cancer are usually put together due to the many commonalities they share. This form of cancer usually develops from a growth in the tissue of the large intestine known as a polyp. If the growth becomes cancerous, it has the potential to spread via blood & lymph vessels.
Colorectal cancer is found in either the colon or the rectum. Colon cancer and rectal cancer are usually put together due to the many commonalities they share. This form of cancer usually develops from a growth in the tissue of the large intestine known as a polyp. If the growth becomes cancerous, it has the potential to spread via blood & lymph vessels.
Nearly all cases of colorectal cancer are of the Adenocarcinomas type, although there can sometimes be others. Adenocarcinomas start in the cells responsible for producing mucus used in the lubrication of the large intestine.
The study that was published in the Journal of the National Career Institute involved around 13,000 patients. It was conducted by the Harvard TH Chan School of Public Health, the National Cancer Institute, and the American Cancer Society, and they found that the increase of vitamin D took away about 31% of the risk.
It has been known that Vitamin D is important in the health of human bones. The testings found that those with a deficiency of the vitamin in their blood had a higher chance of developing colorectal issues. As mentioned by Stephanie Smith-Warner, a Harvard epidemiologist who was part of the study, the individuals with increased percentage above recommended bone-health levels were linked to the lowest rate of colorectal cancer.
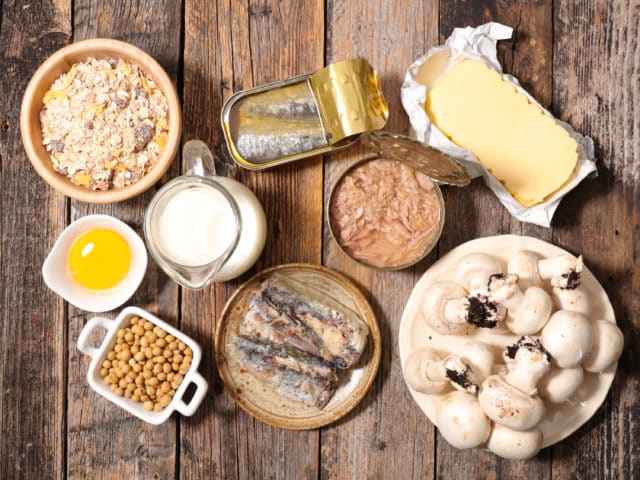
You can get vitamin D through fatty fish such as salmon and trout, milk and orange juice that are fortified with vitamin D, and some dietary supplements. Sun exposure can also heighten vitamin D levels, but because of the risk of contracting skin cancer, it is not highly recommended.